A Solar Micro-Grid as a Community Resource Through Market Participation Using Optimal Time-Switching
In collaboration with the West Atlanta Watershed Alliance, we developed a reinforcement learning (RL)-based system to control a solar microgrid and participate in the energy market. We used a Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) agent to find optimal battery and market actions, under local power demand and battery constraints. The video demonstrates a small, physical microgrid and battery managed by our RL agent, simulating peak/off-peak demand patterns and power prices. The agent autonomously switches between battery and grid usage, optimizing both power delivery and profitability while ensuring local availability.
View Blog PostView Slide Presentation
The TikTok Effect: Causal Roles of Public Opinion in Firearm Acquisition
We conducted a pilot study to collect and analyze TikToks related to #guncontrol. Using zero-shot text classification, we separated the videos into time series representing pro- and anti-regulation content. Applying the PCMCI framework, we performed a statistical causal analysis between TikTok discourse and background checks for firearm purchases. Our results quantify the relationship between social media discourse and firearm acquisition trends in the U.S. This image highlights the time series of social media activity, including spikes in posts following mass shootings.
View Poster Presentation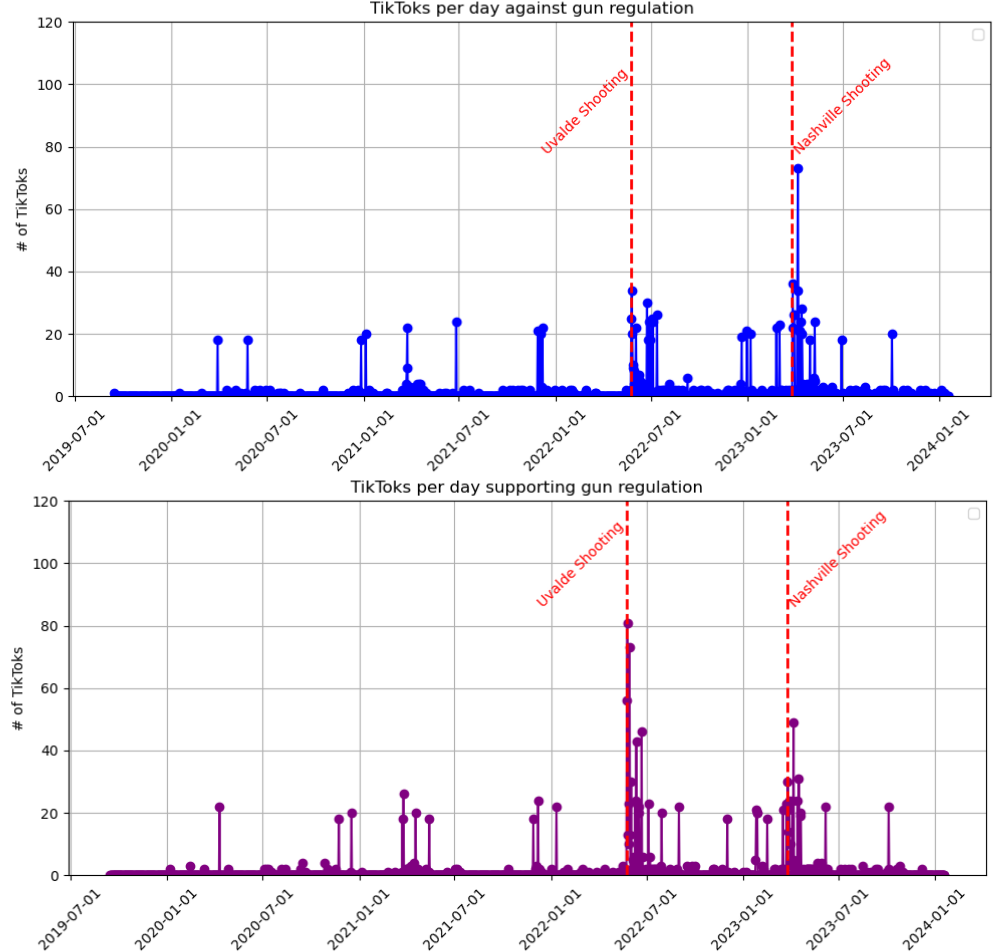
Agent-Based Modeling of Gun Ownership Trends in New York City
To support efforts to reduce gun violence, we analyzed factors driving gun purchases in New York City. Using U.S. Census data, historical redlining maps, and CDC gun-related death statistics, we created an agent-based model of NYC. Our model tests the hypothesis that gun purchases are influenced by crime rates, social influence, and demographic-based social grouping. Specifically, gun purchases are modeled as an "infection" that spreads in a network when a local or social rule is triggered. Each NYC census tract is a node, and the spread of gun purchases is simulated across the network.
View Poster Presentation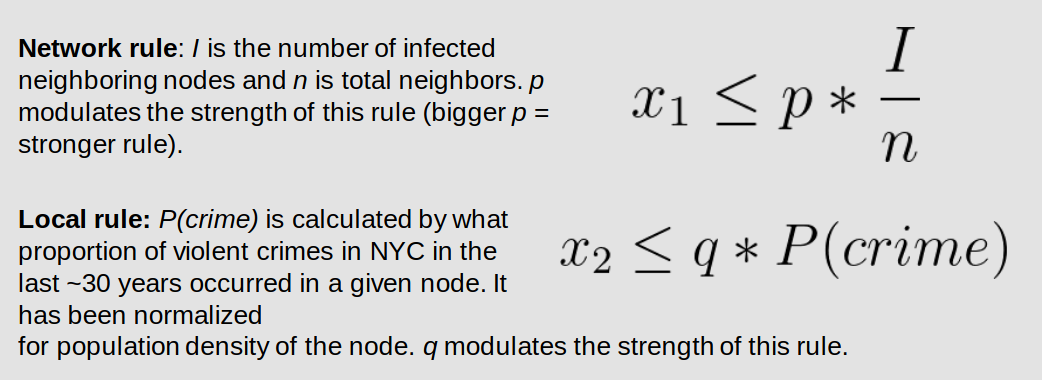
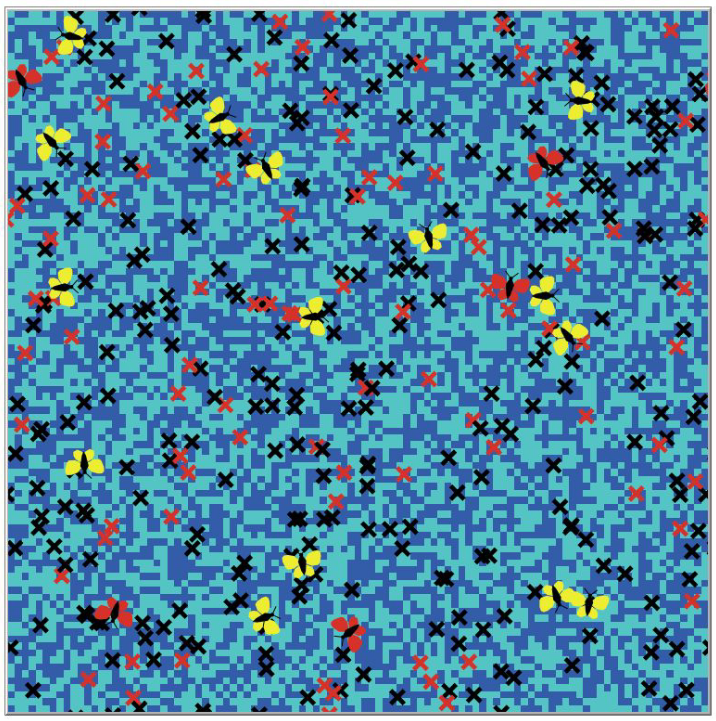
Modeling Predator-Prey Relationships in the Presence of a Multi-Species Parasite
We developed an agent-based simulation of predator-prey interactions based on the Lotka-Volterra equations, investigating the effects of a multi-species parasite. The parasite infects both predator and prey species but only impacts the prey. Our simulation shows the movement and interactions between predators (represented by butterflies), prey (shown as "x" symbols), and their food sources (light-blue squares). Infected units are colored red. Over generations, the simulation evaluates the population dynamics and stability of both predator and prey in the presence of the parasite.
View Slide Presentation